Table Of Content
These trends can be important for identifying causes and risk factors for diseases. A limitation of using this design is that it requires a large sample size. Additionally, the cost of conducting the study may be costly in terms of participant recruitment, the number of staff to conduct the research, and the collection, storage, and analysis of the outcome measurements. Moreover, some conditions (i.e., breast cancer, chronic obstructive disease), despite being relatively common, could occur at low rates in any given evaluation period and not provide meaningful results.
University of Utah
All the cases of heart disease and stroke were diagnosed at the fifth year follow-up. During the scheduled evaluation periods, investigators count the incidence or the number of participants who develop the outcome of interest (i.e., heart disease and stroke). Both terms can provide additional information about the exposure of interest (smoking, nonsmoking) by calculating the risk ratio and rate ratio (Alexander, 2015). As shown in tables 6 and and7,7, there is notable variation among the ethnic groups in intake of both foods and nutrients. Ecologic comparisons of these findings with the corresponding ethnic-sex-specific cancer incidence rates in table 1 already suggest possible relations worth testing at the individual level as cases accrue in the cohort over the next several years. For example, many reports have suggested that the intake of fiber may protect against colorectal cancer (35–37).
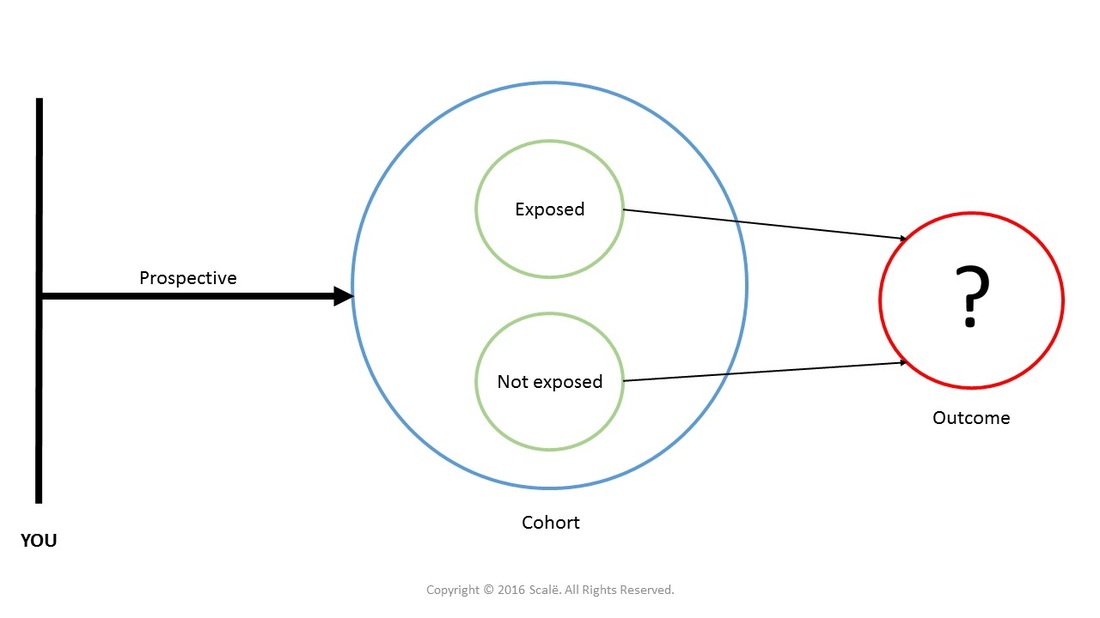
Prospective Cohort Studies
It is quite possible that individuals participating in a cohort study may not be correctly classified – some exposed individuals may be classified as unexposed and the other way round. If the misclassification of the exposure or the outcome is random or nondifferential, then the two groups will be similar and the estimates from the study will be biased towards the null. Thus, we will underestimate the association between the exposure and the outcome. If, however, the misclassification is differential or nonrandom, then the estimates may be biased toward the null, away from the null, or may be an appropriate estimate. The latest is the Millennium Cohort Study, which is following 19,000 babies born in the U.K. In addition to data on the health of these children and their parents, the study is also looking into child behavior and cognitive development, as well as a range of social factors.
The Danish Cohort Study of Psoriasis and Depression
This interplay of cognitive, behavioural, affective and physiological responses is thought to be self-maintaining; symptoms and perpetuating factors sustain each other in a vicious circle. Their disability-stress-coping model describes that the stressors faced by children with a chronic disease are multifaceted and that several personal and family risk- and protective factors are influential. Their focus is on adaptation, which is defined as changeable age-appropriate behaviour. Second, they add that a distinction should be made between intrapersonal factors and interpersonal or social-ecological factors.
Pain site persistence and changes from childhood to adolescence: a prospective cohort study Pediatric Research - Nature.com
Pain site persistence and changes from childhood to adolescence: a prospective cohort study Pediatric Research.
Posted: Mon, 15 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Recruitment and follow-up procedures
A nationwide cohort study on the association between intensive care treatments and mental distress linked psychiatric ... - Nature.com
A nationwide cohort study on the association between intensive care treatments and mental distress linked psychiatric ....
Posted: Sat, 24 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
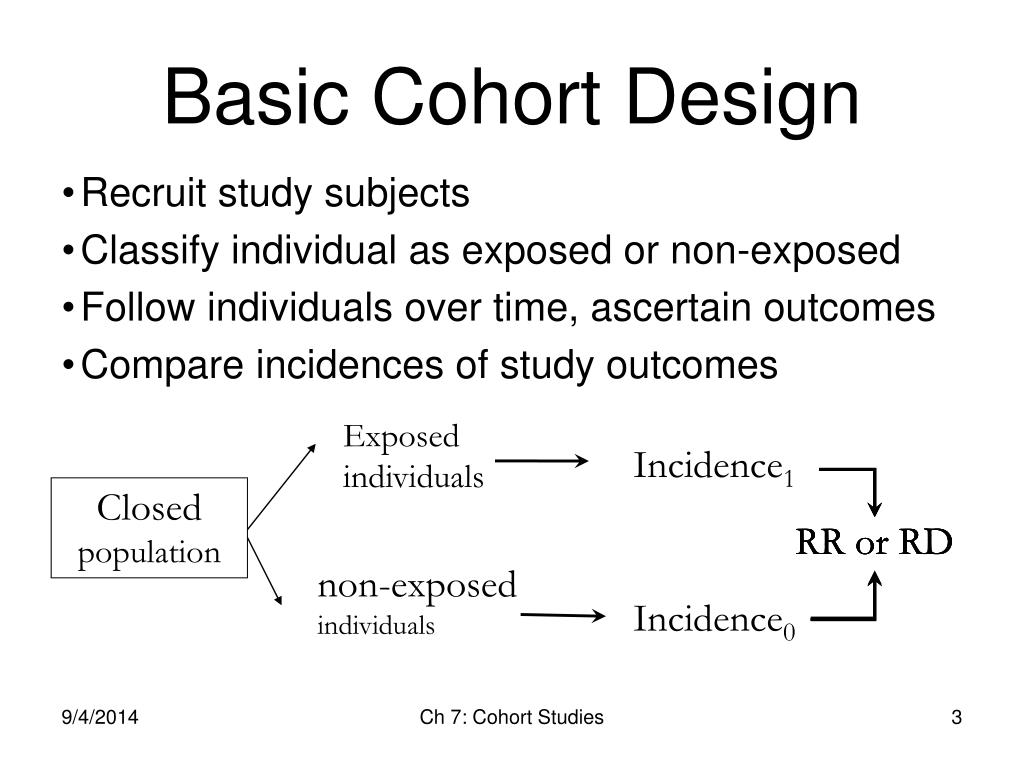
For a prospective cohort study, researchers identify a topic they want to study. They then design the study and recruit the participants that will best help them study the topic. The cohort design is an appropriate method to determine the incidence of a health outcome or an event.
Cohorts are also selected based on exposure and non-exposure status (Setia, 2016). Additionally, the cohort can be divided based on exposure categories at study entry. The questionnaire was designed for self-administration and for processing by optical scanning. Eight frequency categories for foods and nine for beverages were included, together with three (in a few instances four) choices of portion size. As an additional aid to quantification, photographs showing selected foods in representative portion sizes were provided at the head of several pages of the questionnaire. It was important to collect portion size information not only because of significant variations among individuals, but also because of significant variations in the typical serving sizes consumed by different ethnic groups.
Girls Club of Los Angeles
What we can say with confidence is that software shares are in a technical correction, and other equities cohorts that we care about are not far behind. Not only that, in deferring to the women in their lives, these investors weren’t even consulting the right demographic cohorts. By Elizabeth Yuko, PhDYuko has a doctorate in bioethics and medical ethics and is a freelance journalist based in New York. The Dunedin Longitudinal Study, started in 1975, has been studying the thousand people born in Dunedin, New Zealand, in 1972–1973.
Another diet cohort in the United States (22) has also used drivers' license files to identify study participants; other cohorts in the United States and elsewhere (23–27) used different sampling frames. Currently, several cohorts are being assembled across different populations and countries of Europe in order to investigate the role of nutrition in cancer (28). Because the methodologies for sampling and data collection vary across the participating centers, a calibration study, based on 24-hour diet recalls, has been included (29). This is analogous to the calibration study included in the present cohort, which is designed both to reduce measurement error and to permit valid comparisons across the different populations (19). All data is originating from children under treatment at the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital Utrecht (WKZ).
It is based at the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital (WKZ) in the Netherlands and has been running since December 2016. Children with a chronic condition (e.g. cystic fibrosis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, chronic kidney disease, or congenital heart disease) as well children with medically unexplained fatigue or pain in a broad age range (2–18 years) are included, as well as their parent(s). Data are collected from parents (of children between 2 and 18 years) and children (8–18 years), as well as data from their electronic health record (EHR). Primary outcome measures are fatigue, daily life participation, and psychosocial well-being, all assessed via patient- and proxy-reported outcome measures. Generic biological/lifestyle, psychological, and social factors were assessed using clinical assessment tools and questionnaires.
For most disease groups, such as cystic fibrosis, every child with this disease is seen only in a university medical centre. Some diseases that may know a milder disease course, such as inflammatory bowel diseases, are also seen in other clinics, so in these disease groups, this may affect generalizability. This cohort aims to assess fatigue, daily life participation, and psychosocial well-being as primary outcomes across children with various chronic condition from childhood to early adulthood. Clinical assessments as well as patient- and proxy-reported biological, psychological, and social factors are used as determinants. We distinguished the determinants as predisposing, direct stressors or mediating factors and considered which of these factors could be a possible treatment target.
An advantage of prospective cohort studies is that all relevant variables can be thought ofin advance, and data related to these variables can be accurately measured and recorded bytrained study staff. Disadvantages are that prospective cohort studies are expensive toconduct and take long to complete; in fact, the investigators who analyze the data may bethe successors of those who started the study. For practical reasons related to expense andeffort, prospective cohorts are mostly smaller than retrospective cohorts. For a retrospective cohort study, researchers analyze a group of people who already have certain characteristics. For example, they might look at a group of older adults with heart disease. Then they would analyze data about the group members’ medical history to see what factors could have contributed.
To improve health outcomes for Indigenous youth by increasing awareness of substance use prevention, strengthen youth protective factors and reduce barriers to addressing root causes of substance use through youth activism, mentorship and peer education in the Sierra Nevada Foothills. To strengthen the leadership skills of youth of color in Humboldt County through leadership training, coaching and substance use disorder prevention to increase health and life outcomes for youth. To increase leadership development of Southeast Asian youth in Alameda County through youth activism, leadership development, mentorship and mental health services that connect intersectional issues of intergenerational trauma, poverty, racism, incarceration, deportation and substance use. To promote healing, leadership and advocacy skills of youth in Placer County to advance policy change in education, mental health, substance abuse prevention and juvenile justice. Over time, several disease groups within the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital in The Netherlands have joined.
Large cohorts, so identified, will have high statistical power to examinehypotheses of interest. There are advantages to this design, however, as retrospective studies are much cheaper and faster because the data has already been collected and stored. Like case-control and cohort studies, cross-sectional studies are also used in epidemiology to identify exposures and outcomes and compare the rates of diseases and symptoms of an exposed group with an unexposed group. This was a prospective cohort study that ran from 1951 to 2001, investigating the association between smoking and the incidence of lung cancer. Because of the longitudinal nature of these studies, it is common for participants to drop out and not complete the study. The loss of follow-up in cohort studies means researchers are more likely to estimate the effects of an exposure on an outcome incorrectly.
We found in preliminary studies, for example, that nearly one-half of the subjects in each ethnic-sex group selected either the small or large portion size when given a choice, and thus would likely have been misclassified if assigned a standard medium portion. The portion size options on the questionnaire were based on typical serving sizes for each single food or grouping of foods as reflected in the original 3-day measured food records. In Hawaii, names that do not appear on any of these lists primarily identify Caucasians (Whites), whereas in Los Angeles, names that do not occur on any of these lists primarily identify Caucasians or African-Americans. Because it was not possible to distinguish between the latter two groups by this approach, we categorized the census tracts of Los Angeles County by the proportion of African-American residents (9). In addition, we obtained lists of names of African-Americans in California age 65 years and older from the HCFA files. Thus, by a combination of selective sampling from drivers' license files, census tracts with ≥65 percent African-Americans, and the HCFA files, we were able to access the appropriate ethnic populations for the study.
To carry out prospective cohort studies, scientists identify a group of people to study and plan the research in advance, collecting data over time. In retrospective cohort studies, scientists use data that are already available for a particular group. In continuing with the example from above, the calculated rate was 0.016 (see Table 1). The result indicates that 0.016 cases of heart disease and stroke per person-year occurred in the sample, with a rate ratio of 5.2. This result indicates that heart disease and stroke rates were 5.2 times greater in the exposed group than in the unexposed group.
A primary limitation of this study is that the available dataset may be incomplete, inaccurate, or measurements undertaken that do not match the research question (Hulley, 2013). In other words, the investigator(s) do not have control over the data collection methods and procedures. Long-term surveillance for cancer incidence and mortality in this cohort will be accomplished in several ways.

No comments:
Post a Comment